| Corrugated board | [German version] |
Table of contents |
|
| General: | ||
| Product information | ||
| Packaging | ||
| Transport | ||
| Container transport | ||
| Cargo securing | ||
Product information
Product name
| German | Wellpappe |
| English | Corrugated board |
| French | Carton ondulé |
| Spanish | Cartón ondulado |
| CN/HS number * | 4808 10 ff. |
(* EU Combined Nomenclature/Harmonized System)
Product description
Corrugated board consists of one or more plies of fluted paper which is glued onto paper or cardboard. A distinction is drawn between single and multi-wall corrugated board:
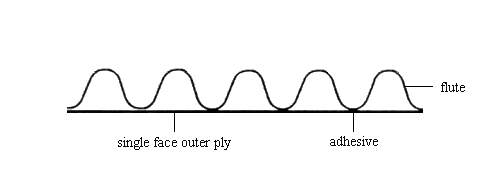
Figure 1: Single face corrugated board consists of one ply of fluted paper which is glued onto paper or cardboard.
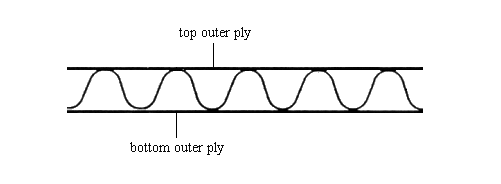
Figure 2: Single wall corrugated board consists of one ply of fluted paper which is glued between two plies of paper or cardboard (also known as double face corrugated board).
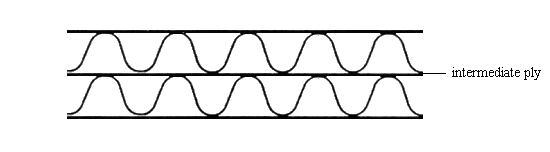
Figure 3: Double wall corrugated board consists of two plies of fluted paper which are glued together by one ply of unfluted paper or cardboard and the exposed outer surfaces of which are each covered with one ply of paper or cardboard.
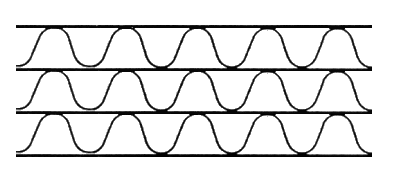
Figure 4: Tri-wall corrugated board consists of three plies of fluted paper which are glued together by two plies of paper or cardboard and the outer surfaces of which are likewise each covered with one ply of paper or cardboard.
Quality / Duration of storage
As is clear from the structure of the various types of corrugated board, they differ most with regard to strength, which increases with the number of plies and/or the quality of the paper used. The strength of corrugated board is determined by the following three characteristics:
| Bursting strength [kPa] | |
| Puncture resistance [J] | |
| Edgewise crush resistance [kN/m] |
The strengths are divided into classes which are defined in DIN standard 55468.
Cartons are usually made from double wall and single wall corrugated board. Cartons made from high strength corrugated board, generally tri-wall (or ultra-heavy) corrugated board, are used for transport operations involving severe climatic conditions and mechanical stresses and for those involving heavier cargoes. Moreover, corrugated board made with moisture-resistant glue and wet strength paper is used in particular for maritime transport.
Intended use
Corrugated board exhibits excellent strength at a low basis weight (175 g/m²). It is very good at absorbing pressure and impact loads and corrugated board is thus used as a material for shipping cartons and for padding fragile goods. Even heavy vehicle parts, such as gearboxes, are transported in high strength corrugated board cartons with an integrated pallet.
Back to beginning
Packaging
Corrugated board is transported in rolls (circumferential packaging with edge protectors). Corrugated board which has already been converted into cartons is transported flat on pallets once provided with edge protectors and secured with plastic strapping.
Back to beginning
Transport
Symbols
 General cargo |
Means of transport
Truck, ship (specially designed for transporting paper), railroad
Container transport
Transport in standard containers , subject to compliance with limits for water content of goods, packaging and flooring.
Cargo handling
It is imperative that the goods be protected from moisture (rain, snow) during cargo handling, as there is a risk of losses caused by swelling and tearing of individual layers.
Incorrect handling during loading and unloading and storage entails the risk of snagging. As a consequence, the paper layers become unusable over the depth of the snags. They are then fit merely to be torn off (stripped down) and used as waste paper.
Incorrect cargo handling may result in distortion of rolls (ovalization). Rolls exhibiting marked ovality can no longer be used for printing and have to be rewound.
Cargo handling of rolls should be performed only with special cargo handling gear and forklift trucks with roll clamps.
Stowage factor
| 2.40 m³/t (rolls, unpackaged) [1] |
Stowage space requirements
Holds must be swept absolutely clean and smooth, to prevent any possibility of damage to the ends. The goods must be protected from any possible leakage from hydraulic lines. In addition, the holds must be protected against ingress of moisture.
Segregation
Packing paper
Cargo securing
In order to ensure safe transport, the cargo must be stowed and secured in the means of transport in such a manner that it does not slip or shift during transport. It must not be damaged by other articles or items of cargo.
For cargo securing, see also chapter entitled Paper trade in the GDV Cargo Securing Manual.
Back to beginning
Risk factors and loss prevention
RF Temperature
Corrugated board requires particular temperature, humidity/moisture and possibly ventilation conditions (SC VI) (storage climate conditions) .
Most favorable travel temperature range: 0 – 25°C [1]
Optimum travel temperature: 20°C [1]
During cargo handling, temperatures below 0°C are also permissible for short periods. The goods must be protected from heat sources.
Back to beginning
RF Humidity/Moisture
Corrugated board requires particular temperature, humidity/moisture and possibly ventilation conditions (SC VI) (storage climate conditions) .
| Designation | Humidity/water content | Source |
| Relative humidity | 65 – 70% | [1] |
| Water content | 8 – 14% | [1] |
| Maximum equilibrium moisture content | 70% | [1] |
Corrugated board must be protected from all moisture, such as rain, snow, condensation water, seawater, extremely high levels of relative humidity or damp stacking surfaces. Optimum relative humidity is 50% in a tropical climate and 65% in a temperate climate.
As corrugated board is mainly made from vegetable fibers, it is hygroscopic and has a tendency to swell. Improper storage or care of the cargo may result in dimensional changes (swelling), distortion (waviness) and reduced strength (tearing). This damage is irreversible, since drying leads to warping due to inner tensions and to staining (drying rings) or to bursting/cracking of the rolls.
Cargo sweat is particularly likely to occur during voyages from cold to hot climates or during unloading in tropical ports if the goods were not sufficiently warmed up during the voyage and were exposed to the hot ambient air upon opening of the hatch covers or container doors.
Corrugated board rolls must not be stowed in a hold with other goods which release moisture.
Back to beginning
RF Ventilation
Corrugated board requires particular temperature, humidity/moisture and possibly ventilation conditions (SC VI) (storage climate conditions) .
Recommended ventilation conditions: air exchange rate: 6 changes/hour (airing), if the dew point of the external air is lower than the dew point of the hold air.
On voyages from cold to hot climates (Scandinavian ports, Continental ports – tropical unloading ports in Africa, Asia), every possible opportunity for warming the corrugated board must be used to avoid cargo sweat.
Back to beginning
RF Biotic activity
This risk factor has no significant influence on the transport of this product.
Back to beginning
RF Gases
This risk factor has no significant influence on the transport of this product.
Back to beginning
RF Self-heating / Spontaneous combustion
Corrugated board is combustible and should therefore be protected from flying sparks. Smoking must be strictly prohibited. The fire point is 258°C, the ignition temperature 427°C. When stacked, it has a tendency to heat-induced spontaneous combustion.
Unlike CO2, water and foam cause considerable cargo losses due to wetting and swelling when used as fire-extinguishing agents.
Back to beginning
RF Odor
| Active behavior | Corrugated board does not release any odor. |
| Passive behavior | It is sensitive to unpleasant and/or pungent foreign odors. |
Back to beginning
RF Contamination
| Active behavior | Corrugated board is a very clean cargo. |
| Passive behavior | Corrugated board is extremely sensitive to contamination by dust, dirt, fats and oils. Soiling damage is caused by dirty set-down surfaces during precarriage, storage, on the wharf and in the hold/container, by soiled hold or container walls and residues from earlier cargoes on the floor, walls, spar ceilings, underdeck beams or hatch cover girders. Stow the cargo away from colorants, acids, chemicals, tar and fats/oils. |
Back to beginning
RF Mechanical influences
Corrugated board is sensitive to mechanical influences such as pressure, impact and friction. Excessive pressure, for example, compresses the corrugated plies, so reducing strength.
Back to beginning
RF Toxicity / Hazards to health
This risk factor has no significant influence on the transport of this product.
Back to beginning
RF Shrinkage / Shortage / Theft
This risk factor has no significant influence on the transport of this product.
Back to beginning
RF Insect infestation / Diseases
This risk factor has no significant influence on the transport of this product.
Back to beginning
